What is HDMI Bandwidth: Complete Beginner-Friendly Guide
Published: 23 Jan 2026
HDMI bandwidth controls the amount of data that moves from a device to a display. Every video frame, audio signal, and color detail travels through this bandwidth.
When the bandwidth is high, the cable carries more information, which results in sharper resolution, smoother motion, and accurate colors. If the bandwidth is low, the screen locks to lower quality settings.
This guide explains HDMI bandwidth in detail with simple explanations, technical clarity, and helpful tables.
What Is HDMI Bandwidth?
HDMI bandwidth refers to the total data rate an HDMI cable and HDMI port can transfer each second. It includes video signals, audio signals and metadata. Higher bandwidth supports higher resolutions, higher refresh rates and deeper color formats.
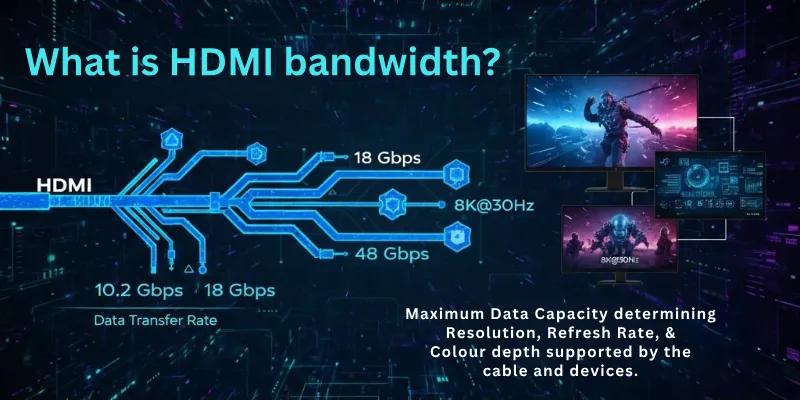
Bandwidth decides how much visual and audio data the cable can handle without signal drops or reduced quality.
Why HDMI Bandwidth Matters
HDMI bandwidth affects every performance layer of your display system. It influences:
- Maximum supported resolution
- Maximum supported refresh rate
- HDR performance
- Color depth
- Chroma subsampling
- Gaming performance
- Signal stability
- Future compatibility
If your HDMI bandwidth is low, the display cannot reach its full potential even if the screen supports better specifications.
How HDMI Bandwidth Works
The data flow depends on five factors:
- Pixel count
- Frames per second
- Color depth
- HDR metadata
- Compression type
The HDMI cable must stay within the maximum bandwidth limit of the HDMI version. If your signal exceeds it, the system reduces quality automatically. This reduction can appear as lower refresh rate, disabled HDR or washed out colors.
Shapes And Types Of HDMI Connectors
HDMI connectors come in different shapes, but they follow the same general data standards.
HDMI Connector Types:
- Type A Standard HDMI: Used on televisions, monitors, consoles and PCs. This is the most common connector.
- Type C Mini HDMI: Used on cameras, tablets and portable devices. It is smaller and lighter.
- Type D Micro HDMI: Used on action cameras and very small devices. It is compact and fits tight spaces.
- Type E Automotive HDMI: Used in cars and vehicle infotainment systems. It includes a locking mechanism.
Note: The shape does not change the bandwidth. Only the HDMI version changes the bandwidth.
HDMI Versions And Their Bandwidth
Each HDMI version increases the maximum bandwidth capacity. Below is a clear table for comparison.
| HDMI Version | Maximum Bandwidth | Supported Video Formats | Best Use Case |
| HDMI 1.4 | 10.2 Gbps | 1080p 120 Hz, 4K 30 Hz | Basic TVs and old monitors |
| HDMI 2.0 | 18 Gbps | 4K 60 Hz, 1440p 144 Hz | Movies and mid range gaming |
| HDMI 2.0b | 18 Gbps | Enhanced HDR formats | 4K HDR streaming |
| HDMI 2.1 | 48 Gbps | 4K 120 Hz, 8K 60 Hz | High end gaming and modern TVs |
HDMI 2.1 offers the largest jump with 48 Gbps which supports high refresh rate gaming and advanced HDR.
HDMI Bandwidth And Resolution
Higher resolution needs more bandwidth because it carries more pixels in each frame.
| Resolution | Typical Refresh Rate | Bandwidth Demand | HDMI Version Needed |
| 1080p | 60 Hz | Low | HDMI 1.4 or higher |
| 1440p | 144 Hz | Medium to High | HDMI 2.0 or higher |
| 4K | 60 Hz | High | HDMI 2.0 or higher |
| 4K | 120 Hz | Very High | HDMI 2.1 |
| 8K | 60 Hz | Extreme | HDMI 2.1 |
When the resolution increases, the bandwidth climbs quickly.
HDMI Bandwidth And Refresh Rate
Refresh rate controls how many frames your screen shows each second. Higher refresh rates increase HDMI bandwidth requirements.
How Refresh Rate Affects Bandwidth:
- 60 Hz uses lower bandwidth
- 120 Hz doubles the frame load
- 144 Hz and above increases the load even more
- 240 Hz needs advanced compression or high speed HDMI cables
If the bandwidth is not enough, the display drops to a lower refresh rate automatically.
HDMI Bandwidth And Color Depth
Color depth increases the amount of data per pixel. This directly impacts HDMI bandwidth.
| Color Depth | Bits Per Channel | Visual Quality | Bandwidth Impact |
| 8 bit | 256 shades | Standard color | Low |
| 10 bit | 1024 shades | Required for HDR | Medium |
| 12 bit | 4096 shades | Professional grade | High |
Higher bit depth improves gradient smoothness and HDR accuracy but it increases the bandwidth.
HDMI Bandwidth And Chroma Subsampling
Chroma subsampling reduces color information to lower bandwidth usage. It affects text clarity and fine color detail.
| Format | Color Data Quality | Usage | Bandwidth Impact |
| 4:4:4 | Full color | PC monitors and text use | High |
| 4:2:2 | Medium color | Broadcasting | Medium |
| 4:2:0 | Reduced color | Movies and streaming | Low |
If you want sharp text on monitors, 4:4:4 is ideal.
Compressed vs Uncompressed HDMI Signals
HDMI 2.1 supports DSC compression which allows high frame rate and high resolution together.
| Type | Description | Advantage | Limitation |
| Uncompressed | Full data transfer | Best quality | Needs high bandwidth |
| DSC Compressed | Light compression | Allows higher frame rates | Needs HDMI 2.1 |
DSC does not noticeably reduce visual quality because it preserves fine detail.
Where HDMI Bandwidth Is Used
HDMI bandwidth plays a key role in modern devices.
Like:
- Televisions
- Monitors
- Gaming consoles
- PC graphics cards
- Laptops
- Blu ray players
- Cameras
- Streaming boxes
- Projectors
- Automotive displays
- Home theater receivers
Every display system depends on proper HDMI bandwidth to show high-quality output.
How To Pick The Right HDMI Bandwidth For Your Setup
Use this rule-based guide.
- For Movies And Streaming: HDMI 2.0 handles smooth 4K HDR playback.
- For Gaming Consoles: Use HDMI 2.1 to unlock 4K 120 Hz or higher refresh rates.
- For PC Monitors: 1440p 144 Hz and above requires HDMI 2.0 or higher.
- For 8K TVs: Only HDMI 2.1 supports full 8K performance.
Signs Your HDMI Bandwidth Is Not Enough
Low bandwidth can cause visible issues.
- Screen flicker
- HDR not working
- Locked refresh rate
- Washed out colors
- Random screen blackouts
- Reduced resolution
- Signal loss
These issues usually appear when the cable or port cannot handle the required data load.
How To Check HDMI Cable Bandwidth
You can confirm the bandwidth in several ways.
- Look for labels such as High Speed or Ultra High Speed
- Check the packaging
- Test on high resolution and high refresh rate
- Use certified cables for long distances
- Match the cable version with the display requirements
Ultra High Speed HDMI cables always support 48 Gbps and full HDMI 2.1 performance.
Final Words
In this guide we have covered everything about HDMI bandwidth in clear detail.
You learned what HDMI bandwidth means, how it works, what shapes and versions exist, how resolution and refresh rate affect it, how color depth and chroma subsampling change the data load and how compression plays a role in modern HDMI setups.
This guide also explained how to choose the right cable, how to identify bandwidth problems and how to match HDMI versions with your specific display needs. With this knowledge you can pick the right HDMI cable and get the best performance from any TV, monitor or gaming system.
FAQs: HDMI Bandwidth
Here are some of the most commonly asked questions related to the HDMI bandwidth:
1. What affects HDMI bandwidth?
HDMI bandwidth changes when you increase resolution, refresh rate and color depth. Higher settings need more data, so the HDMI bandwidth must match your display needs. If the HDMI bandwidth is low, your screen lowers the resolution or refresh rate. Always check your HDMI version before choosing display settings.
2. Does HDMI cable length reduce bandwidth?
Yes, long HDMI cables weaken the signal and reduce HDMI bandwidth performance. When the cable gets too long, the data flow becomes unstable. This can cause flickers or lower image quality. A certified High Speed or Ultra High Speed HDMI cable fixes most length issues.
3. Can HDMI 2.0 handle 4K at 120 Hz?
No, HDMI 2.0 does not support 4K at 120 Hz. It only supports 4K at 60 Hz because of its limited HDMI bandwidth. You need HDMI 2.1 for full 4K 120 Hz gaming. Modern consoles also need HDMI 2.1 for high refresh rate output.
4. Why does my TV not show HDR even with HDMI 2.0?
HDR needs extra HDMI bandwidth and correct color depth. If the port or cable cannot handle the full HDR signal, the TV disables HDR. Some TVs require HDR to be enabled manually in settings. A strong High Speed HDMI cable improves HDR stability.
5. Does HDMI bandwidth affect gaming?
Yes, HDMI bandwidth affects gaming quality, resolution and refresh rate. Low bandwidth limits smooth gameplay and fast motion clarity. HDMI 2.1 gives the best gaming results because it supports 4K 120 Hz and VRR. Always pair your console with the right HDMI cable.
6. Are all HDMI cables the same?
No, HDMI cables support different bandwidth levels. Standard cables cannot handle modern 4K or 8K signals. Ultra High Speed HDMI cables support 48 Gbps and full HDMI 2.1 features. Choose the cable that matches your display and gaming needs.
7. Can HDMI bandwidth cause signal drops?
Yes, low HDMI bandwidth often causes blackouts and signal loss. When the HDMI cable cannot carry the full data load, the screen resets or shows a weak signal. High resolution and HDR increase the load fast. A higher bandwidth HDMI cable fixes most dropouts.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks