Active or Passive HDMI Cables: Simple Comparison Guide
Published: 24 Nov 2025
Do you ever wonder which HDMI cable is right for your setup: Active or Passive?
Both types look the same, but they work differently, especially when it comes to signal transmission, distance, and power requirements. Choosing the wrong one can lead to signal loss, poor video quality, or unnecessary extra spending.
This guide will focus only on the differences between Active and Passive HDMI cables. By the end, you’ll understand which one suits your needs, whether for a home theater, gaming, office, or long-distance setup.
Related Reads:
- What is Active HDMI Cable?
- What is Passive HDMI Cable?
Active vs Passive HDMI Cables: Key Differences
Here are some of the major differences between Active and Passive HDMI cables:
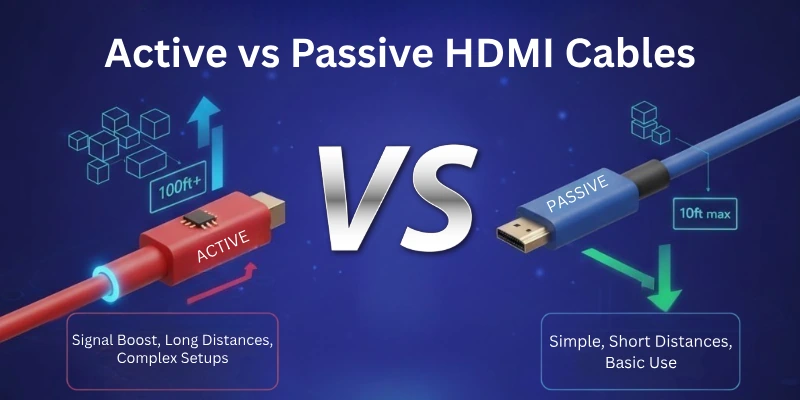
Let’s start.
- Signal Boosting Technology
- Maximum Cable Length
- Power Requirement
- Performance & Stability
- Cable Weight & Flexibility
- Bandwidth & Resolution Support
- Durability & Lifespan
- Interference Resistance
Let me guide you through each difference in detail.
1. Signal Boosting Technology
Signal boosting technology helps to strengthen weak signals so they can travel long distances without losing quality. It is used in many types of cables, including HDMI cables, to improve performance.
Active HDMI Cable (Uses Signal Boosting)
- Has built-in electronics to make the signal stronger.
- Can send signals over long distances without losing quality.
- Needs extra power to work, often from the HDMI port or an external source.
- Helps support high-quality video and audio, even in long cables.
- Works best for setups where the cable needs to be longer than 15 feet.
Passive HDMI Cable (Does Not Use Signal Boosting)
- Does not have any built-in electronics to boost the signal.
- Works well for short distances, usually under 15 feet.
- Does not need extra power, as it directly transfers the signal.
- Might lose signal quality if the cable is too long.
- Best for simple home setups with short connections.
2. Maximum Cable Length
The maximum cable length is how far an HDMI cable can send a signal without losing quality. Longer cables can cause signal loss, so choosing the right type is important.
Active HDMI Cable
- Can send signals over long distances, often up to 50 feet or more.
- Uses built-in electronics to keep the signal strong.
- Works best for home theaters, large conference rooms, and gaming setups that need long cables.
- More reliable for 4K, 8K, and high refresh rate displays over long distances.
- Usually costs more than passive HDMI cables.
Passive HDMI Cable
- Works well for short distances, usually under 15-25 feet.
- Does not have a signal booster, so the quality may drop over long distances.
- Ideal for TVs, gaming consoles, and streaming devices that are close to the display.
- Supports 4K and Full HD, but performance may drop if the cable is too long.
- More affordable and widely available.
3. Power Requirement
Power requirement refers to whether an HDMI cable needs extra power to work properly. Some cables need built-in electronics that require power, while others work without any additional power source.
Active HDMI Cable
- Requires external power to boost the signal.
- Usually draws power from the HDMI port, but some may need a USB power source.
- Helps maintain high-quality video and audio over long distances.
- Some models may require a separate power adapter.
- More complex to set up compared to passive HDMI cables.
Passive HDMI Cable
- Does not require any external power.
- Works directly through the HDMI ports of connected devices.
- Transfers the signal as it is, without boosting it.
- Easier to use—just plug and play.
- Best for short connections where extra power is unnecessary.
4. Performance & Stability
Performance and stability refer to how well an HDMI cable maintains signal quality and prevents interruptions during use.
Active HDMI Cable
- Maintains high-quality signal over long distances.
- Reduces interference and signal loss for 4K/8K content.
- Prevents video flickering, lag, and audio dropouts.
- Works well in high-interference environments.
Passive HDMI Cable
- Stable for short-distance connections.
- Works best within its length limit (usually under 25 feet).
- May experience signal loss over long distances.
- More prone to interference from nearby electronics.
5. Cable Weight & Flexibility
Cable weight affects how easy it is to handle, install, and route around devices. Flexibility determines if the cable can bend without damage, making installation easier in tight spaces.
Active HDMI Cable
- Heavier due to built-in signal boosting components.
- Less flexible, making it harder to bend or manage.
- Not ideal for frequent plugging and unplugging.
- Best for fixed setups like home theaters and professional displays.
- May require more space for proper cable routing.
Passive HDMI Cable
- Lightweight with no extra electronic parts.
- Highly flexible, making installation easier.
- Perfect for tight spaces and cable management systems.
- Great for portable setups like laptops, projectors, and gaming consoles.
- Easier to unplug and move between devices.
6. Bandwidth & Resolution Support
Bandwidth refers to the amount of data a cable can transfer per second, while resolution support determines the highest video quality it can handle, such as 1080p, 4K, or 8K.
Active HDMI Cable
- Supports higher bandwidth for 4K, 8K, and HDR content.
- Maintains smooth video quality over long distances.
- Reduces signal loss, ensuring stable high-resolution output.
- Ideal for high-performance gaming, home theaters, and professional displays.
- Can handle higher refresh rates (e.g., 120Hz, 144Hz) for gaming.

Passive HDMI Cable
- Supports standard bandwidth for 1080p and 4K (at short distances).
- Works best for shorter cable runs (under 15-25 feet).
- May struggle with 8K or high refresh rates over long distances.
- More suitable for TVs, streaming devices, and casual gaming.
- Affordable choice for users who don’t need ultra-high resolution.
7. Durability & Lifespan
Durability refers to how strong the cable is and how well it resists wear and tear. Lifespan is how long the cable lasts before it stops working properly.
Active HDMI Cable
- More fragile due to built-in electronic components.
- Not as resistant to bending or twisting.
- Prone to damage if mishandled or frequently moved.
- Shorter lifespan if used improperly or in high-stress environments.
- Best for fixed setups where the cable stays in one place.
Passive HDMI Cable
- More durable since it has no extra electronic parts.
- Can handle frequent bending and movement without breaking.
- Longer lifespan if properly maintained.
- Great for everyday use, including travel and portable devices.
- Better suited for setups where cables are frequently plugged and unplugged.
8. Interference Resistance
Interference resistance refers to a cable’s ability to avoid signal disruption from external electronic devices, such as Wi-Fi routers, mobile phones, and power cables.
Active HDMI Cable
- Better resistance to interference due to built-in signal processing.
- Minimizes signal loss and distortion, even in environments with many electronic devices.
- Ideal for long-distance connections where interference is more likely.
- Less affected by electromagnetic and radio frequency interference (EMI/RFI).
- Ensures stable transmission for high-quality audio and video.
Passive HDMI Cable
- More prone to interference, especially over longer distances.
- No built-in technology to reduce external signal disruptions.
- May experience flickering or loss of quality if placed near strong electronic signals.
- Better suited for short distances, where interference is minimal.
- Using high-quality shielding can help reduce interference issues.
Pros & Cons Comparison: Active vs Passive HDMI Cables
Here is a quick overview of the pros and cons of both active and passive HDMI cables:
| Feature | Active HDMI Cable (Pros) | Active HDMI Cable (Cons) | Passive HDMI Cable (Pros) | Passive HDMI Cable (Cons) |
| Signal Quality | Boosts signal for long distances | Requires extra power | Works well for short distances | Weaker signal over long distances |
| Maximum Length | Supports long cable runs (30+ feet) | More expensive | Ideal for short setups (under 15 feet) | Limited length before signal loss |
| Power Requirement | Built-in amplifier for stability | Needs power from HDMI or external source | No extra power needed | No signal enhancement available |
| Interference Resistance | Less affected by EMI/RFI | May need shielding for extreme cases | Works fine in low-interference areas | More prone to interference |
| Price | Higher cost due to added technology | More expensive than passive cables | Budget-friendly option | Performance drops over long distances |
Final Verdict: Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between an Active HDMI Cable and a Passive HDMI Cable depends on your specific needs. Here’s a simple breakdown:
Choose an Active HDMI Cable if:
- You need to run HDMI over long distances (more than 15-25 feet).
- You want strong signal quality without interference or loss.
- Your setup includes high-resolution content (4K, 8K) with high refresh rates.
- You don’t mind spending a bit more for better performance.
Choose a Passive HDMI Cable if:
- Your cable length is short (under 15 feet).
- You prefer a simple, plug-and-play connection without extra power.
- Your devices support standard resolutions without signal loss.
- You want a budget-friendly and flexible option for home or office use.
If you’re still unsure, check your devices’ HDMI version and bandwidth requirements. Passive cables are fine for short connections, but active HDMI cables are the better choice for long distances or high-quality signals.
Final Thoughts
We have covered everything you need to know about Active vs Passive HDMI Cables, from how they work to their pros and cons. An active HDMI cable is worth the investment if your setup requires long-distance transmission and high resolutions. On the other hand, for shorter connections and everyday use, a passive HDMI cable works just fine.
Understanding these differences will help you make the best choice for your needs!
FAQs
Here are some of the most commonly asked questions related to active and passive hdmi cables:
It depends on your needs. Passive HDMI cables are great for short distances (under 15 feet) and are budget-friendly. Active HDMI cables are better for long distances because they boost the signal and prevent quality loss.
Yes, active HDMI cables need extra power to boost the signal. They usually draw power from the HDMI port itself, but some may require a separate power source like USB.
You can, but it’s unnecessary. Active HDMI cables are designed for long distances. For short connections, a passive HDMI cable works just fine and is more affordable.
Yes, most active HDMI cables support 4K and even 8K resolutions, depending on their HDMI version. Always check the specifications to make sure it matches your device’s requirements.
Active HDMI cables usually mention “Active” on the packaging or product description. They may also have a built-in chip for signal boosting and sometimes a separate power connection. Passive cables don’t have these extra components.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks